熔断
熔断
文档:https://istio.io/latest/zh/docs/tasks/traffic-management/circuit-breaking/
什么是熔断
熔断(Circuit Breaking)是微服务架构中的一种重要的弹性设计模式,在微服务环境中,不同的服务存在依赖关系,当其中一个依赖的服务出现问题时,可能导致请求积压,从而影响到其他服务和整个系统的稳定性。比如说,B 服务来了 100 个请求,B 需要请求 100 次 A 服务,但是 A 服务故障了,那么每次失败时都会重试一次,那么整体上就一共请求了 200 次。这样就会造成很大的浪费。而熔断器可以检测到这种情况,当检测到 A 服务故障之后,一段时间内所有对 A 的请求都会直接返回错误。
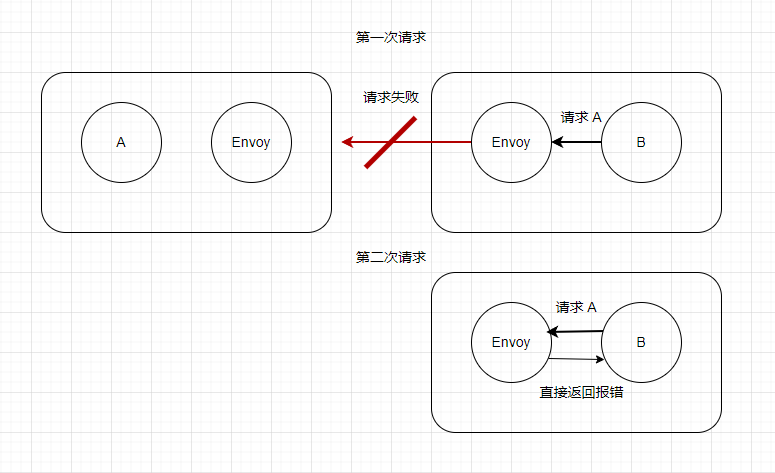
熔断器模式的工作原理如下:
- 正常状态:熔断器处于关闭状态,允许请求通过(熔断器会监控请求的成功和失败率)。
- 故障检测:当失败率达到预先定义的阈值时,熔断器就会启动。
- 熔断状态:熔断器处于打开状态时,将拒绝所有新的请求,并返回错误响应。这可以防止故障级联和给故障服务带来更多的压力。
- 恢复状态:在一段时间后,熔断器会进入半打开状态,允许一部分请求通过。如果这些请求成功,则熔断器将返回到关闭状态;如果仍然存在失败请求,则熔断器继续保持打开状态。
使用熔断器模式可以提高微服务系统的弹性和稳定性。这些工具提供了熔断器模式的实现,以及其他弹性设计模式,如负载均衡、重试和超时等。
示例
创建 httpbin 服务
接下来本节将会使用一个 httpbin 服务,这个服务代码可以在 istio 官方仓库中找到: https://github.com/istio/istio/tree/release-1.17/samples/httpbin
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: httpbin
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: httpbin
labels:
app: httpbin
service: httpbin
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 8000
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: httpbin
type: NodePort
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: httpbin
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: httpbin
version: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: httpbin
version: v1
spec:
serviceAccountName: httpbin
containers:
- image: docker.io/kennethreitz/httpbin
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: httpbin
ports:
- containerPort: 80
接着给 httpbin 创建一个 DestinationRule ,里面配置了熔断规则。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: httpbin
spec:
host: httpbin
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
tcp:
maxConnections: 1
http:
http1MaxPendingRequests: 1
maxRequestsPerConnection: 1
outlierDetection:
consecutive5xxErrors: 1
interval: 1s
baseEjectionTime: 3m
maxEjectionPercent: 100
DestinationRule(目标规则)用于定义访问特定服务的流量策略。DestinationRule 配置中的 trafficPolicy 属性允许为服务指定全局的流量策略,这些策略包括负载均衡设置、连接池设置、异常检测等。
另外,在创建熔断时也可以设置重试次数。
创建访问者服务
在 Istio 服务网格环境下,流量进入网格后会被 Envoy 拦截,接着根据相应的配置实现路由,熔断也是在 Envoy 之间实现的,只有流量经过 Envoy ,才会触发 Istio 的熔断机制。
熔断是服务之间通讯出现的,所以还需要部署一个服务请求 httpbin,才能观察到熔断过程。Istio 官方推荐使用 fortio
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fortio
labels:
app: fortio
service: fortio
spec:
ports:
- port: 8080
name: http
selector:
app: fortio
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: fortio-deploy
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: fortio
template:
metadata:
annotations:
# This annotation causes Envoy to serve cluster.outbound statistics via 15000/stats
# in addition to the stats normally served by Istio. The Circuit Breaking example task
# gives an example of inspecting Envoy stats via proxy config.
proxy.istio.io/config: |-
proxyStatsMatcher:
inclusionPrefixes:
- "cluster.outbound"
- "cluster_manager"
- "listener_manager"
- "server"
- "cluster.xds-grpc"
labels:
app: fortio
spec:
containers:
- name: fortio
image: fortio/fortio:latest_release
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
name: http-fortio
- containerPort: 8079
name: grpc-ping
部署 fortio 之后,进入到 fortio 容器中,执行命令请求 httpbin。
执行命令获取 fortio 的 Pod 名称:
export FORTIO_POD=$(kubectl get pods -n default -l app=fortio -o 'jsonpath={.items[0].metadata.name}')
然后让 Pod 容器执行命令:
kubectl -n default exec "$FORTIO_POD" -c fortio -- /usr/bin/fortio curl -quiet http://httpbin:8000/get
如果上面的命令执行没问题的话,可以通过下面的命令对 httpbin 服务进行大量请求,并且分析请求统计结果。
kubectl -n default exec "$FORTIO_POD" -c fortio -- /usr/bin/fortio load -c 3 -qps 0 -n 20 -loglevel Warning http://httpbin:8000/get
在控制台中可以看到请求返回 200 和 503 的比例
...
Uniform: false, Jitter: false, Catchup allowed: true
IP addresses distribution:
10.110.174.129:8000: 4
Code 200 : 19 (95.0 %)
Code 503 : 1 (5.0 %)
Response Header Sizes : count 20 avg 218.5 +/- 50.13 min 0 max 230 sum 4370
Response Body/Total Sizes : count 20 avg 592.3 +/- 72.79 min 275 max 609 sum 11846
All done 20 calls (plus 0 warmup) 2.510 ms avg, 1039.7 qps