CPU基础知识
对于 Linux 机器,可以用 lscpu、cat /proc/info 等命令查看它的 CPU 信息
展示的信息如下
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Address sizes: 43 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 256
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-255
Vendor ID: AuthenticAMD
BIOS Vendor ID: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Model name: AMD EPYC 7742 64-Core Processor
BIOS Model name: AMD EPYC 7742 64-Core Processor
CPU family: 23
Model: 49
Thread(s) per core: 2
Core(s) per socket: 64
Socket(s): 2
Stepping: 0
Frequency boost: enabled
CPU(s) scaling MHz: 92%
CPU max MHz: 2250.0000
CPU min MHz: 1500.0000
BogoMIPS: 4499.65
Flags: fpu ...
Virtualization features:
Virtualization: AMD-V
Caches (sum of all):
L1d: 4 MiB (128 instances)
L1i: 4 MiB (128 instances)
L2: 64 MiB (128 instances)
L3: 512 MiB (32 instances)
NUMA:
NUMA node(s): 2
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-63,128-191
NUMA node1 CPU(s): 64-127,192-255
Vulnerabilities:
Gather data sampling: Not affected
Itlb multihit: Not affected
L1tf: Not affected
Mds: Not affected
Meltdown: Not affected
Mmio stale data: Not affected
Retbleed: Mitigation; untrained return thunk; SMT enabled with STIBP protection
Spec rstack overflow: Mitigation; Safe RET
Spec store bypass: Mitigation; Speculative Store Bypass disabled via prctl
Spectre v1: Mitigation; usercopy/swapgs barriers and __user pointer sanitization
Spectre v2: Mitigation; Retpolines, IBPB conditional, STIBP always-on, RSB filling, PBRSB-eIBRS Not affected
Srbds: Not affected
Tsx async abort: Not affected
可以看到有 255 个 CPU,但无法看到 CPU 在物理上是怎么分布的(layout)
(1)Package
如下图,package(直译为“封装”)是我们能直接在主板上看到的一个东西,里面封装一个或多个处理器核心(称为 core 或 processor)

(2)Core (processor)
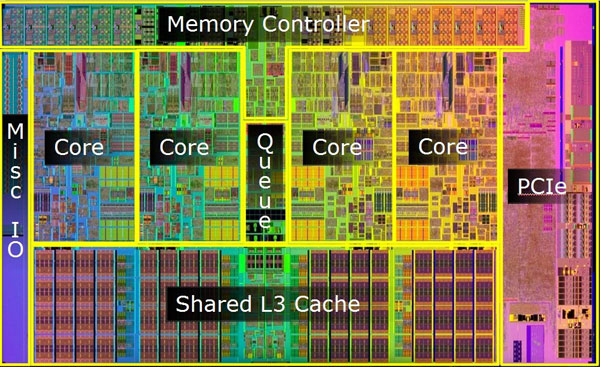
指硬件核心/硬件处理器。一个 package 里面可能会包含多个处理器,如下图所示
或者从芯片视图看:
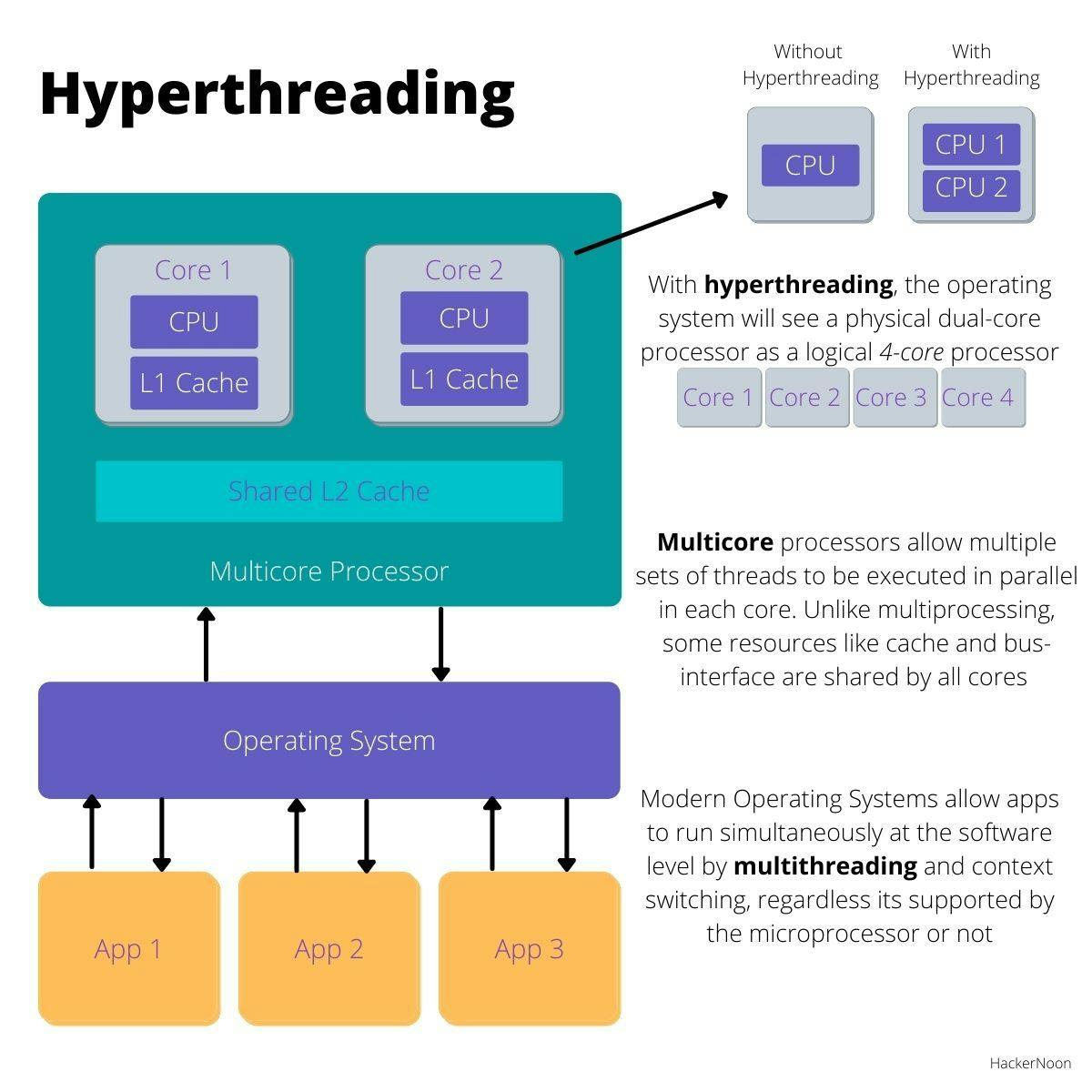
(3)超线程(Hyper-threading)/硬件线程(hardware thread)
大部分 X86 处理器都支持超线程,也叫硬件线程。 如果一个 CORE 支持 2 个硬件线程, 那么启用超线程后, 这个 CORE 上面就有 2 个在大部分情况下都能独立执行的指令流(这 2 个硬件线程共享 L1 cache 等), 操作系统能看到的 CPU 数量会翻倍(相比 CORE 的数量), 每个 CPU 对应的不是一个 CORE,而是一个硬件线程 / 超线程(hyper-thread)
(4)Logical CPU
以上提到的 package、core/processor、hyper-threading/hardware-thread,都是硬件概念。
在任务调度的语境中,所说的 “CPU” 其实是一个逻辑概念。 例如,内核的任务调度是基于逻辑 CPU 来的
- 每个逻辑 CPU 分配一个任务队列(run queue),独立调度
- 每个逻辑 CPU 能独立加载指令并执行
逻辑 CPU 的数量和分布跟 package/core/hyper-threading 有直接关系, 一个逻辑 CPU 不一定对应一个独立的硬件处理器
前面提到的 lscpu 输出中有 Thread(s) per core: 2 说明它启用了超线程/硬件线程
通过工具 cpupower 来看下它的 CPU 分布,执行:
可以得到输出
intel-rapl/intel-rapl:0
0
intel-rapl/intel-rapl:0/intel-rapl:0:0
0
| Mperf || RAPL || Idle_Stats
PKG|CORE| CPU| C0 | Cx | Freq || pack | core || POLL | C1 | C2
0| 0| 0| 20.42| 79.58| 3192||178743488|544543|| 0.00| 3.21| 76.33
0| 0| 128| 0.11| 99.89| 3172||178743488|544543|| 0.00| 5.18| 94.46
0| 1| 1| 24.27| 75.73| 3195||178743488|544543|| 0.00| 2.17| 74.12
0| 1| 129| 0.12| 99.88| 3172||178743488|544543|| 0.00| 5.29| 94.36
0| 2| 2| 59.94| 40.06| 3195||178743488|544543|| 0.05| 26.05| 13.10
0| 2| 130| 0.10| 99.90| 3150||178743488|544543|| 0.00| 3.51| 96.13
...
0| 63| 63| 0.06| 99.94| 2520||178743488|544543|| 0.00| 1.11| 98.79
0| 63| 191| 0.13| 99.87| 2667||178743488|544543|| 0.00| 3.03| 96.50
1| 0| 64| 2.85| 97.15| 3220||178743488|544543|| 0.00| 3.47| 93.60
1| 0| 192| 77.95| 22.05| 3190||178743488|544543|| 0.00| 4.28| 18.62
1| 1| 65| 2.94| 97.06| 3075||178743488|544543|| 0.00| 6.40| 90.53
1| 1| 193| 0.59| 99.41| 2215||178743488|544543|| 0.00| 8.23| 90.87
...
1| 63| 255| 1.35| 98.65| 3143||178743488|544543|| 0.00| 3.58| 95.07
前三列:
- PKG:package,2 个独立的 CPU package(0~1),对应上面的 NUMA;
- CORE:物理核心/物理处理器。每个 package 里 64 个 CORE(0~63);
- CPU:用户看到的 CPU,即上面所说的逻辑 CPU;这台机器启用了超线程(hyperthreading),每个 CORE 对应两个 hardware thread, 每个 hardware thread 最终呈现为一个用户看到的 CPU,因此最终是 256 个 CPU(0~255)
也可以通过 hw-loc 查看硬件拓扑,里面能详细到不同 CPU 的 L1/L2 cache 关系,执行:
可以得到输出
Machine (2003GB total)
Package L#0
NUMANode L#0 (P#0 995GB)
L3 L#0 (16MB)
L2 L#0 (512KB) + L1d L#0 (32KB) + L1i L#0 (32KB) + Core L#0
PU L#0 (P#0)
PU L#1 (P#128)
L2 L#1 (512KB) + L1d L#1 (32KB) + L1i L#1 (32KB) + Core L#1
PU L#2 (P#1)
PU L#3 (P#129)
L2 L#2 (512KB) + L1d L#2 (32KB) + L1i L#2 (32KB) + Core L#2
PU L#4 (P#2)
PU L#5 (P#130)
L2 L#3 (512KB) + L1d L#3 (32KB) + L1i L#3 (32KB) + Core L#3
PU L#6 (P#3)
PU L#7 (P#131)
...
对应关系为
Machine (2003GB total)
# PKG 0
Package L#0
NUMANode L#0 (P#0 995GB)
L3 L#0 (16MB)
# Core 0
L2 L#0 (512KB) + L1d L#0 (32KB) + L1i L#0 (32KB) + Core L#0
# Logical CPU 0
PU L#0 (P#0)
# Logical CPU 128
PU L#1 (P#128)
# Core 1
L2 L#1 (512KB) + L1d L#1 (32KB) + L1i L#1 (32KB) + Core L#1
# Logical CPU 1
PU L#2 (P#1)
# Logical CPU 129
PU L#3 (P#129)
...